Guide to Building Effective Preventive Maintenance Schedules
Preventive measures are the frontline defense against operational disruptions in equipment and facility maintenance. At the heart of this strategy lies the symbiotic relationship between Preventive Maintenance and Preventive Maintenance Schedules. PM schedules are the tactical implementation of broader preventive maintenance plans, providing a structured framework for the regular upkeep of equipment and assets.
Preventive Maintenance Schedules offer a proactive approach to maintenance, ensuring that equipment is regularly inspected, serviced, and optimized. By systematically addressing potential issues before they escalate, organizations can increase equipment reliability, minimize unplanned downtime, and reduce operational costs. The foresight embedded in preventive maintenance schedules transforms maintenance from a reactive burden into a strategic asset.
What is a Preventive Maintenance Schedule?
A Preventive Maintenance Schedule is a planned and systematic program of maintenance activities designed to prevent the occurrence of equipment failures or breakdowns. The primary goal of preventive maintenance is to keep equipment in good working condition and prevent unplanned downtime by addressing potential issues before they lead to failures. This type of maintenance is proactive and aims to extend the lifespan of equipment, improve reliability, and reduce overall maintenance costs.
The Preventive Maintenance Schedule is typically created based on factors such as equipment manufacturer recommendations, historical performance data, and industry best practices. The schedule outlines specific tasks, their frequencies, and the resources required for each maintenance activity. Preventive Maintenance Schedules can be managed using various tools, including Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS). PM schedules are essential for work settings where equipment reliability is very important, such as manufacturing plants, facilities management, and transportation.
Components of a Preventive Maintenance Schedule
1. Inspection Tasks
Preventive Maintenance Schedules hinge on well-structured inspection tasks. These tasks are designed to identify and address wear, tear, or anomalies before they can evolve into critical problems.
1.1 Regular Visual Inspections
Routine visual inspections form the bedrock of any effective Preventive Maintenance Schedule. Maintenance personnel systematically examine equipment, looking for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Visual inspections are not just a surface-level examination; they are a proactive measure to catch issues at their inception.
1.2 Equipment Testing
Beyond visual scrutiny, equipment testing is an important component of Preventive Maintenance Schedules. This involves subjecting machinery to various tests and diagnostics to ensure all components are functioning within specified parameters. By systematically evaluating performance, potential faults can be identified and addressed before they compromise operational integrity.

2. Routine Maintenance Tasks
Routine maintenance tasks are activities scheduled at regular intervals and are aimed at preserving the optimal functioning of equipment over time.
2.1 Lubrication
Preventive Maintenance Schedules include regular lubrication of moving parts to minimize friction, reduce wear and tear, and ensure the longevity of critical components. This simple yet vital task is a cornerstone of equipment preservation.
2.2 Filter Replacements
Air, oil, and fuel filters play a pivotal role in maintaining the cleanliness of various systems. Regular filter replacements, as outlined in the Preventive Maintenance Schedule, prevent contaminants from compromising the efficiency and performance of equipment. This proactive measure safeguards against potential breakdowns caused by clogged or inefficient filters.
2.3 Calibration
Preventive Maintenance Schedules allocate specific time for calibration tasks, ensuring that equipment remains accurate and functions within prescribed tolerances. This not only enhances the reliability of measurements but also contributes to overall operational accuracy.
3. Scheduled Downtime for Maintenance
While routine tasks are essential, Preventive Maintenance Schedules also designate periods for more comprehensive and in-depth maintenance activities.
3.1 Overhauls
Scheduled overhauls involve a comprehensive examination and refurbishment of equipment. This could include disassembly, replacement of worn components, and a thorough inspection of the entire system. Overhauls are strategically planned to coincide with the end of a machine's lifecycle or when performance indicators signal the need for extensive attention.
3.2 Equipment Upgrades
Technological advancements and changing operational requirements may necessitate equipment upgrades. Preventive Maintenance Schedules earmark time for assessing the need for upgrades, ensuring that systems remain aligned with industry standards and organizational objectives.

Importance of a Well-Structured Preventive Maintenance Schedule
1. Improved Equipment Reliability
One of the primary advantages of a well-structured Preventive Maintenance Schedule is the significant improvement in equipment reliability. Regular inspections, routine maintenance tasks, and proactive measures ensure that machinery operates at peak efficiency. By addressing potential issues before they escalate, organizations create an environment where equipment breakdowns become rare occurrences, bolstering the overall reliability of critical assets.
2. Minimized Unplanned Downtime
Unplanned downtime is the bane of operational efficiency. A well-thought-out Preventive Maintenance Schedule acts as a shield against unforeseen disruptions. By systematically addressing wear, tear, and potential malfunctions, organizations can substantially reduce the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns. This not only preserves productivity but also contributes to a smoother operational flow and customer satisfaction.
3. Enhanced Safety Standards
Safety is important in any operational setting, and a well-structured Preventive Maintenance Schedule plays a pivotal role in upholding rigorous safety standards. By identifying and rectifying potential safety hazards during routine inspections and maintenance tasks, organizations create a safer working environment. This proactive approach not only protects personnel but also mitigates the risk of accidents and injuries associated with malfunctioning equipment.
4. Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Control
Contrary to the misconception that preventive maintenance results in unnecessary expenses, a well-structured Preventive Maintenance Schedule is cost-effective. The upfront investment in preventive measures is often dwarfed by the potential costs associated with reactive maintenance, emergency repairs, and downtime. By proactively addressing issues before they escalate, organizations can control maintenance costs, extend the lifespan of equipment, and allocate resources more efficiently, contributing to long-term budget stability.
Difference between Preventive Maintenance Plan and Preventive Maintenance Schedule
1. Preventive Maintenance Plan
1.1 Strategic Approach to Maintenance
A Preventive Maintenance Plan is the strategic backbone of an organization's approach to maintenance. It encompasses a holistic view of the maintenance goals and strategies that an organization adopts to ensure the reliability and longevity of its equipment and assets. This plan is not confined to specific tasks or timelines but rather sets the overarching framework for how maintenance will be approached within an organization.
1.2 Inclusion of Overall Maintenance Goals and Strategies
Within the Preventive Maintenance Plan, organizations outline their overarching maintenance objectives. This includes defining the scope of preventive measures, determining the criticality of various equipment, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the maintenance program. The plan serves as a guide for the entire maintenance team, aligning efforts with the broader organizational objectives.
2. Preventive Maintenance Schedule
2.1 Tactical Implementation of the Plan
In contrast, a Preventive Maintenance Schedule is the tactical implementation of the broader Preventive Maintenance Plan. While the plan sets the strategic direction, the schedule translates these strategic goals into practical, day-to-day activities. It provides a structured timeline and framework for executing specific maintenance tasks, ensuring that the strategic goals outlined in the plan are carried out in a systematic and organized manner.
2.2 Specific Tasks, Frequencies, and Resources Allocated
Within the Preventive Maintenance Schedule, each task is broken down into specific activities, outlining the what, when, and how of maintenance. It details the tasks that need to be performed, the frequencies at which they should occur, and the resources allocated for their execution. This level of detail allows for the systematic execution of the preventive measures outlined in the broader plan, ensuring that each task contributes to the overall maintenance strategy.
Types of Preventive Maintenance Schedules
Preventive Maintenance Schedules come in various forms, each tailored to meet specific organizational needs and the nature of the equipment being managed.
1. Time-Based Schedule
1.1 Regular Intervals (Daily, Weekly, Monthly)
Time-based schedules are perhaps the most common preventive maintenance approach. This involves routine inspections and maintenance activities scheduled at fixed intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly. This ensures that equipment receives regular attention, reducing the likelihood of wear and malfunction.
1.2 Seasonal or Annual Tasks
Seasonal or annual tasks are incorporated into preventive maintenance schedules to address equipment needs that may vary with changing environmental conditions. For example, heating systems might require specific checks before the winter season or cooling systems before the summer.
2. Usage-Based Schedules
2.1 Maintenance Triggered by Equipment Usage
Usage-based schedules tie maintenance activities directly to equipment utilization. This approach ensures that maintenance is performed based on the actual workload the equipment experiences. For instance, a forklift might undergo maintenance after a certain number of operating hours.
2.2 Adjustments Based on Operational Data
Usage-based schedules can be refined by integrating operational data. This involves analyzing equipment performance metrics and adjusting maintenance intervals accordingly. By leveraging real-time data, organizations can optimize maintenance to align with the equipment's actual usage patterns.
3. Predictive Maintenance Schedules
3.1 Utilizing Data and Analytics for Predictive Tasks
Predictive maintenance schedules leverage advanced data analytics and technology to predict when equipment maintenance is required. By monitoring equipment condition and performance, organizations can anticipate potential issues before they occur. This minimizes downtime and reduces the need for unnecessary preventive tasks.
3.2 Condition Monitoring
Condition monitoring is a key component of predictive maintenance schedules. It involves the continuous monitoring of equipment parameters, such as vibration, temperature, or oil quality. Any deviation from the norm triggers maintenance actions. This proactive approach allows for targeted interventions precisely when needed.
These different types of preventive maintenance schedules offer organizations flexibility in designing strategies that align with their unique operational demands. By selecting the most suitable type or combining elements from multiple approaches, organizations can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of their preventive maintenance programs.
Steps to Create an Effective Preventive Maintenance Schedule
The following are key steps to ensure the creation of an efficient preventive maintenance schedule:
1. Asset Inventory and Categorization
1.1 Identifying and Listing All Equipment
The initial step involves conducting a thorough inventory of all equipment within the organization. This includes machinery, tools, and any other assets requiring maintenance. This comprehensive list serves as the foundation for the preventive maintenance schedule.
1.2 Categorizing Equipment Based on Criticality
Once identified, equipment is categorized based on its criticality to operations. Critical assets that, if failed, would significantly impact production or safety receive a higher priority in the preventive maintenance schedule. This categorization helps in allocating resources effectively.
2. Establishing Maintenance Frequencies
2.1 Determining Optimal Intervals for Preventive Tasks
Each category of equipment requires a tailored approach to maintenance frequencies. Some machinery may need frequent check-ups, while others can adhere to less frequent intervals. This step involves evaluating manufacturer recommendations, industry best practices, and historical performance data to determine optimal maintenance intervals.
2.2 Adjusting Frequencies Based on Equipment Usage
Maintenance needs aren't static. Adjustments based on equipment usage patterns enhance the precision of the schedule. For instance, a machine operating under heavy load or in harsh conditions may require more frequent maintenance. Regularly reassessing and adapting frequencies ensure alignment with real-world usage.
3. Documentation and Record-Keeping
3.1 Creating a Comprehensive Equipment Database
A detailed and organized equipment database is the foundation of any efficient preventive maintenance schedule. This involves recording critical information for each asset, including specifications, manufacturer details, maintenance history, and any unique requirements. Modern tools like CMMS software can streamline this process.
3.2 Logging Maintenance Activities and Findings
Accurate record-keeping during and after maintenance activities is essential for ongoing improvement. Documenting performed tasks, parts replaced, and any abnormalities observed creates a valuable resource for future reference. It aids in trend analysis, highlights recurring issues, and contributes to the refinement of maintenance strategies.
Using CMMS Software for Building and Managing PM Schedules
1. Streamlining the Preventive Maintenance Process
1.1 Automated Scheduling
CMMS software automates the scheduling process, allowing organizations to create, adjust, and manage PM schedules with ease. This automation ensures that tasks are consistently executed at the right intervals, minimizing the risk of oversights or missed maintenance activities.
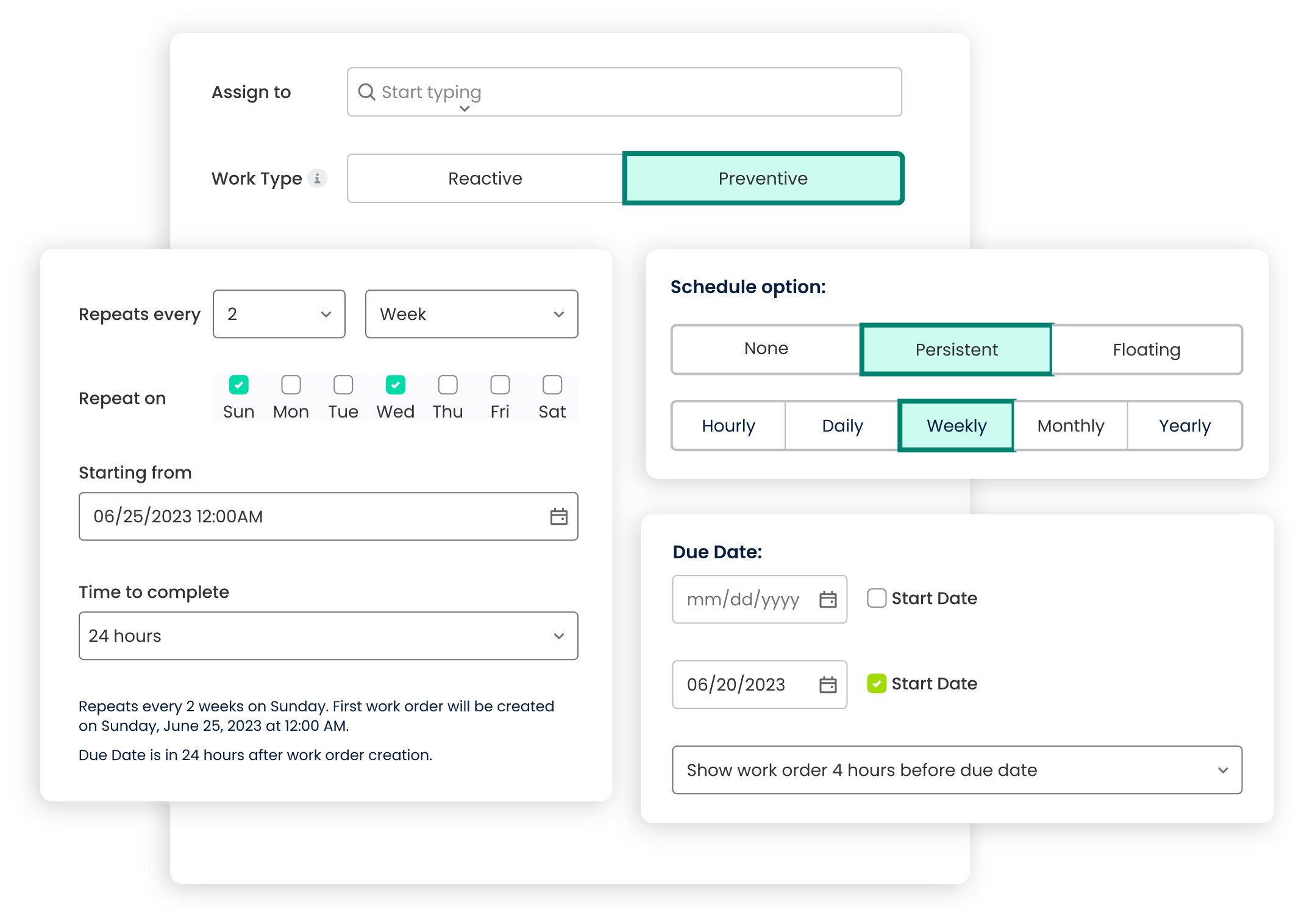
1.2 Calendar-Based Alerts
A CMMS utilizes calendar-based alerts to notify maintenance teams of upcoming preventive tasks. These alerts can be configured to send reminders for inspections, routine maintenance, or any other scheduled activity. This feature contributes to better planning and adherence to the established schedule.
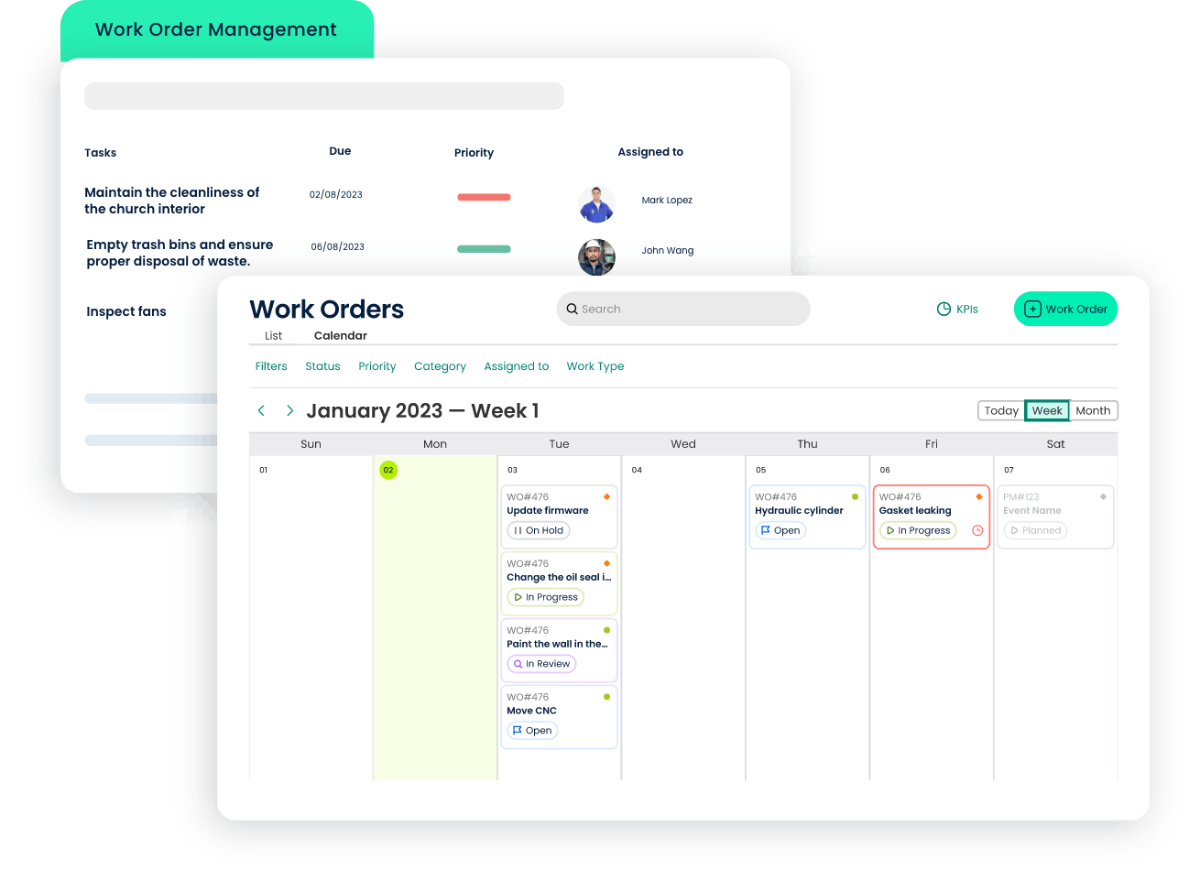
2. Enhanced Resource Management
2.1 Resource Allocation and Optimization
CMMS software provides a centralized platform for managing resources. It allows organizations to allocate manpower, materials, and tools efficiently for each preventive maintenance task. This ensures that the right resources are available when needed, preventing delays in the execution of maintenance activities.
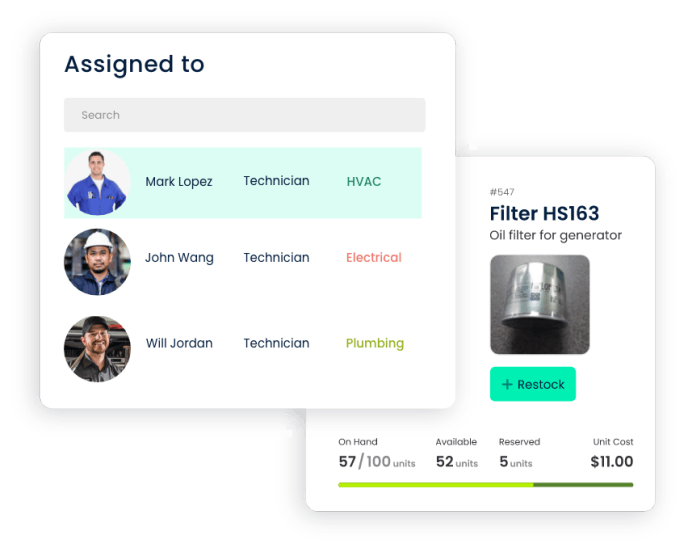
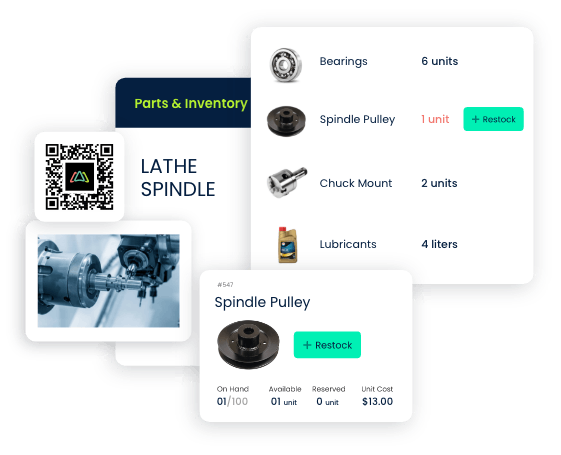
2.2 Inventory Management
Efficient preventive maintenance requires access to the right spare parts. CMMS software assists in managing inventory levels by tracking stock levels, automating reordering processes, and ensuring that required parts are readily available. This reduces downtime associated with waiting for necessary components.
3. Comprehensive Documentation and Reporting
3.1 Maintenance History Tracking
CMMS systems maintain a detailed history of all maintenance activities. This includes records of completed preventive tasks, inspections, and any issues identified and addressed. This historical data is invaluable for trend analysis, identifying recurring problems, and making informed decisions for future maintenance planning.
![]()
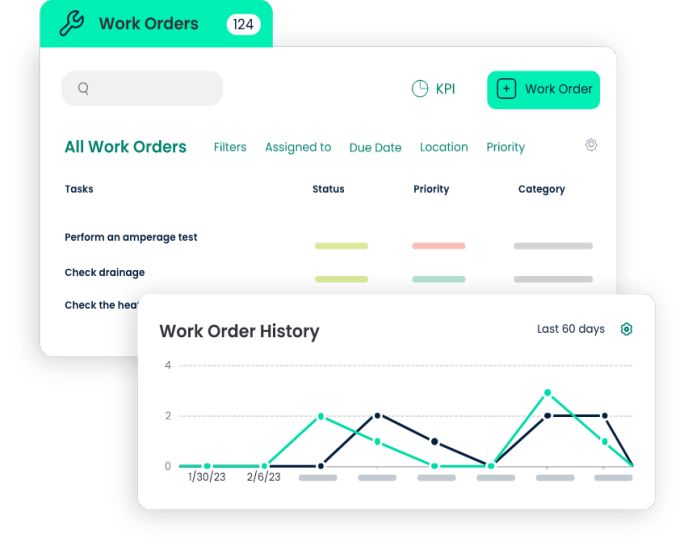
3.2 Customizable Reporting
Organizations can generate customizable reports through CMMS software, providing insights into the performance of preventive maintenance schedules. These reports can include key performance indicators, adherence to schedules, and the overall effectiveness of maintenance efforts. This data-driven approach aids in continuous improvement.
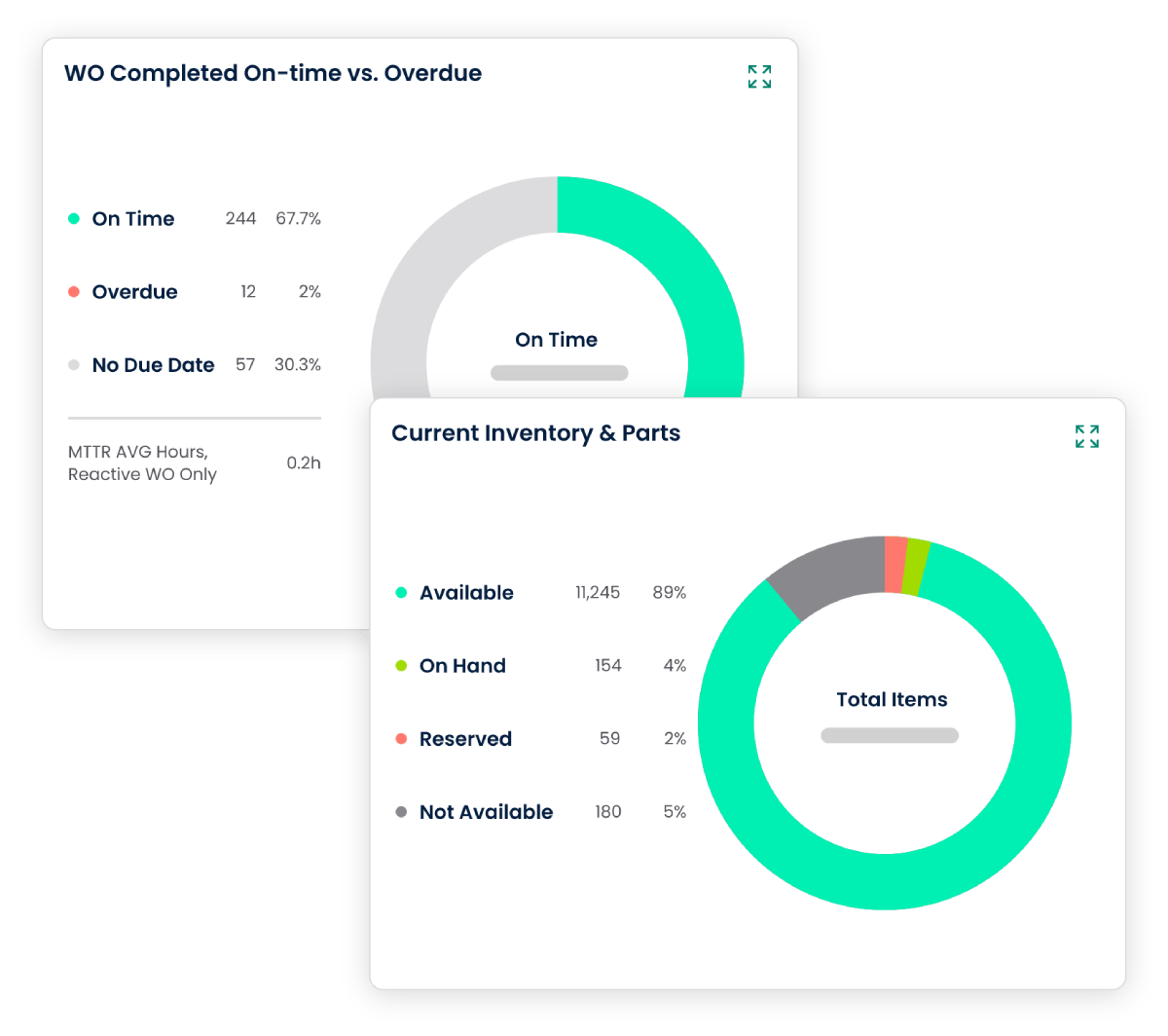
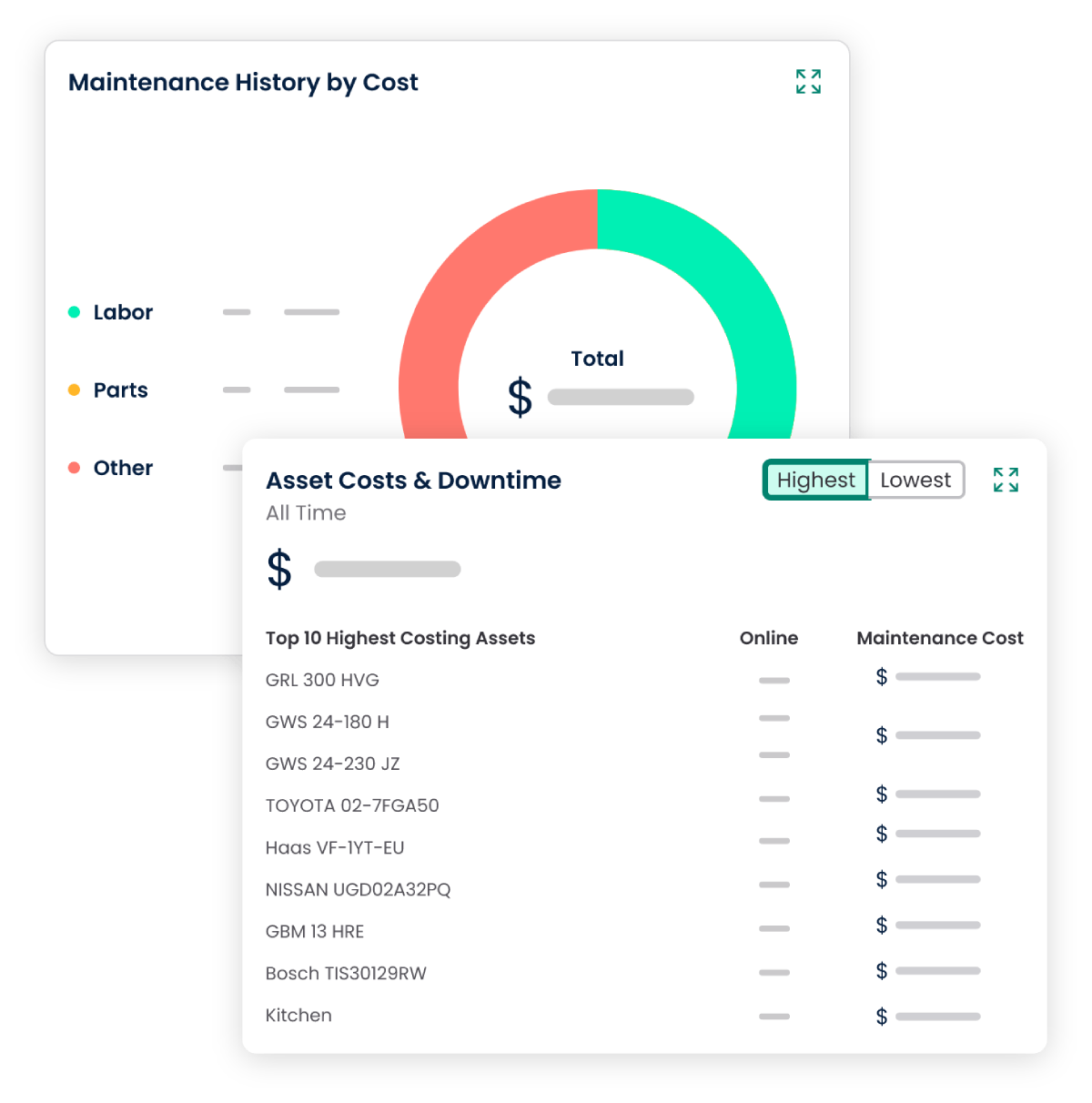
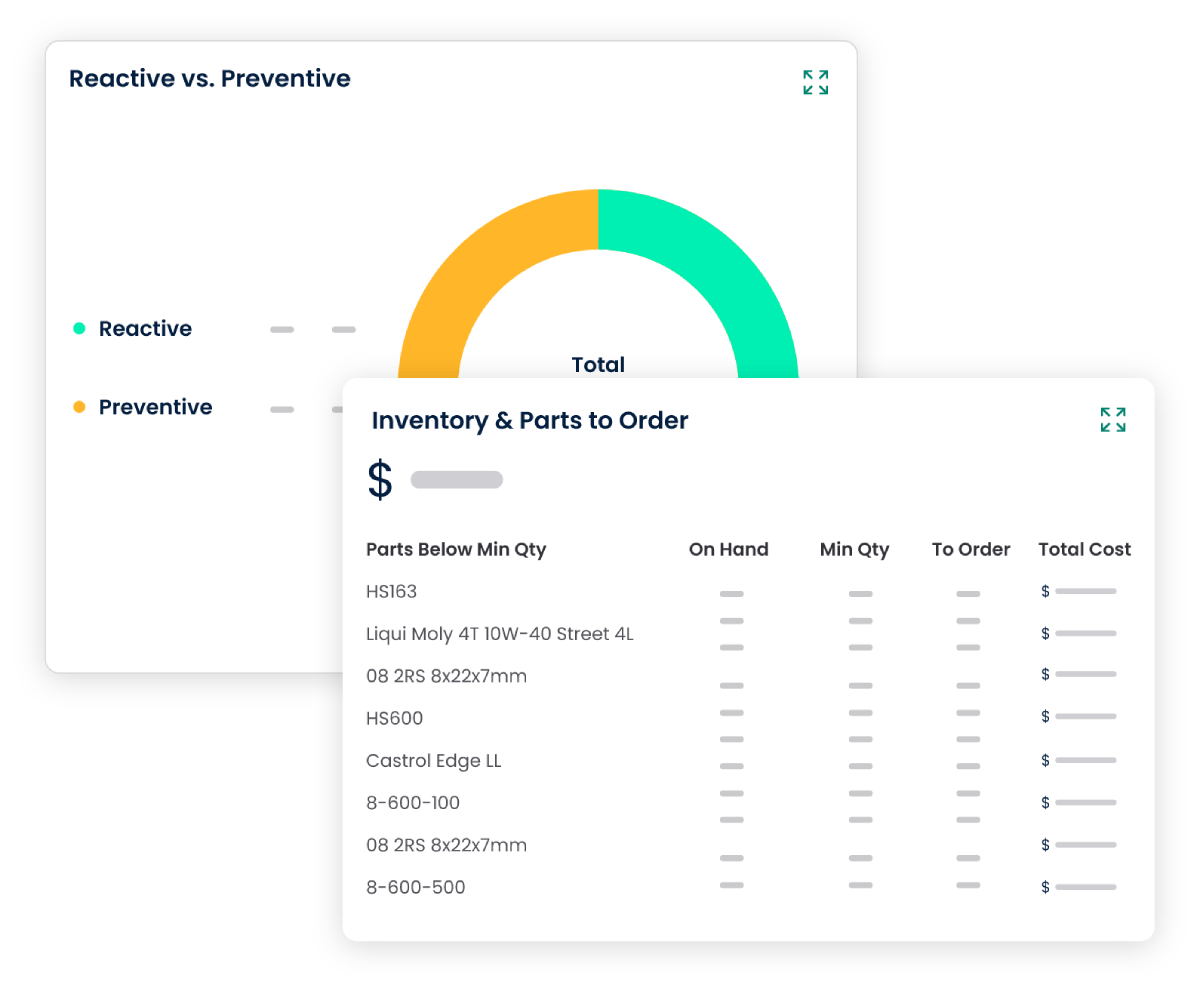
4. Scalability and Adaptability
4.1 Scalability for Growth
CMMS solutions are designed to scale with the growth of an organization. Whether managing a few assets or an extensive facility, the software can adapt to the evolving needs of the organization, accommodating changes in the scale and complexity of preventive maintenance schedules.
4.2 Integration Capabilities
CMMS integration with other enterprise systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, enhances the overall efficiency of preventive maintenance. CMMS software's ability to seamlessly integrate with existing systems ensures a cohesive and interconnected maintenance management ecosystem.
Leveraging CMMS software for building and managing Preventive Maintenance schedules empowers organizations to optimize their maintenance processes. The automation, resource management capabilities, comprehensive documentation, and adaptability offered by CMMS contribute to a proactive and efficient maintenance strategy. As technology continues to advance, the integration of CMMS is becoming a strategic imperative for organizations aiming to elevate their maintenance practices.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Keep Reading
School facilities are busy, high-traffic places. On average, 45.8 million students attend ...
10 Feb 2026
There is also no shortage of acronyms in the maintenance world. So, here is one more to add ...
6 Feb 2026
You may be wondering: if you are already using CMMS software in your organization, aren’t ...
5 Feb 2026
Although artificial intelligence (AI) has been around since the mid-1950s, it wasn’t until ...
3 Feb 2026
Fire safety is often treated as a compliance checkbox rather than an ongoing operational ...
30 Jan 2026
Schools are regarded as places of learning where children are exposed to the basics of ...
29 Jan 2026
Facility maintenance, much like running a business, defies one-size-fits-all solutions. The ...
27 Jan 2026
When we think of inspections, we usually think about ensuring regulatory compliance and ...
23 Jan 2026
In maintenance operations, having the right spare parts in the right amount and at the right ...
22 Jan 2026
The relentless march of technology continuously reshapes the industry landscape, and with it, ...
20 Jan 2026
New Year’s resolutions tend to focus on lifestyle or financial changes, often aimed at making ...
16 Jan 2026
Now that 2026 has arrived, we’ll see that manufacturing trends will matter more than ever, as ...
15 Jan 2026
Now that 2026 is here, it’s a great time to assess what can be achieved in maintenance ...
13 Jan 2026
2026 is when the role of a CMMS Software in capital allocation comes to the fore. This is the ...
12 Jan 2026
Choosing the right work order software is no longer optional for maintenance teams in 2026. ...
6 Jan 2026
By 2026, CMMS platforms will no longer be the limiting factor in maintenance performance. ...
30 Dec 2025
Spare parts management within maintenance can make the difference between a problem-free ...
16 Dec 2025
Every maintenance team eventually faces the same question: When should we repair, and when ...
12 Dec 2025
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) software has become a cornerstone for organizations aiming ...
12 Dec 2025
Unexpected equipment breakdowns can disrupt operations, increase repair costs, and reduce ...
11 Dec 2025





